Vitamin C plays many critical roles in our body, and it’s also considered an essential dietary micronutrient - while most animals are able to make their own vitamin C, humans can’t. We must get all we need from what we eat (1)
This article is takes you through why this micronutrient is so important, what happens in deficiencies, and where to find foods rich in vitamin C.
Vitamin C Benefits
Some early studies show that people who have enough vitamin C have a lower risk of developing some serious chronic health problems such as high blood pressure, eye disease, stroke and cardiovascular disease.
Vitamin C may be having such a positive influence on these diseases by helping our blood vessels to stay in good shape. While some people may claim that vitamin C may help to prevent cancer, there hasn’t yet been any good evidence to show that this is true.
This definitely doesn’t mean that taking vitamin C will cure heart disease. However these studies due support the importance of getting enough of this important micronutrient to reduce the risk of many health problems (2).
What Does Vitamin C Do?
1. Immune System Support
You may have heard that taking vitamin C may help cure your cold. While there is unfortunately no cure for the common cold, regular use of vitamin C may help you to recover more quickly when you’re feeling sick (3).
2. Tissue Development & Maintenance
Vitamin C helps make a protein called collagen. Collagen is an important part of our bones, connective tissues, blood vessels, tendons, ligaments and more. Vitamin C is absolutely needed to help create and maintain the tissues that make us who we are (4).
3. Wound Healing
When tissue is damaged, adequate amounts of vitamin C helps to heal this tissue, partially by helping to create new collagen.
4. Antioxidant Actions
Antioxidants are important in helping minimize and repair damage caused by toxins, such as smoke or radiation. On a cellular level, these toxins produce damaging products called free radicals.
Antioxidants like vitamin C help to neutralize free radicals. This is why it’s recommended that people who smoke consume more vitamin C than people who aren’t exposed to as much smoke.
5. Helps Iron Absorption
Vitamin C helps iron to be absorbed. This is important because we must have iron for our red blood cells to be created. Iron deficiency is a common cause of anemia (low red blood cells) (5).
6. Vitamin C for Skin
This micronutrient is so important for skin because it helps to provide enough collagen for our skin maintenance and also works as an antioxidant to help protect our skin from ultraviolet (UV) damage (6).
7. Vision Support
Vitamin C seems to help support our eyes. It’s been shown to help decrease the risk of developing macular degeneration and might help prevent cataracts from forming (3)
Vitamin C Foods
Many fruits and vegetables are all vitamin C rich foods. This is especially true in citrus fruits, such as oranges. Unfortunately cooked vegetables don’t contribute significant amounts of the vitamin as heat destroys water soluble vitamins like vitamin C.
Like many of the other important micronutrients, it is also added to many commonly consumed foods such as cereals (referred to as ‘fortified’).
Foods High in Vitamin C
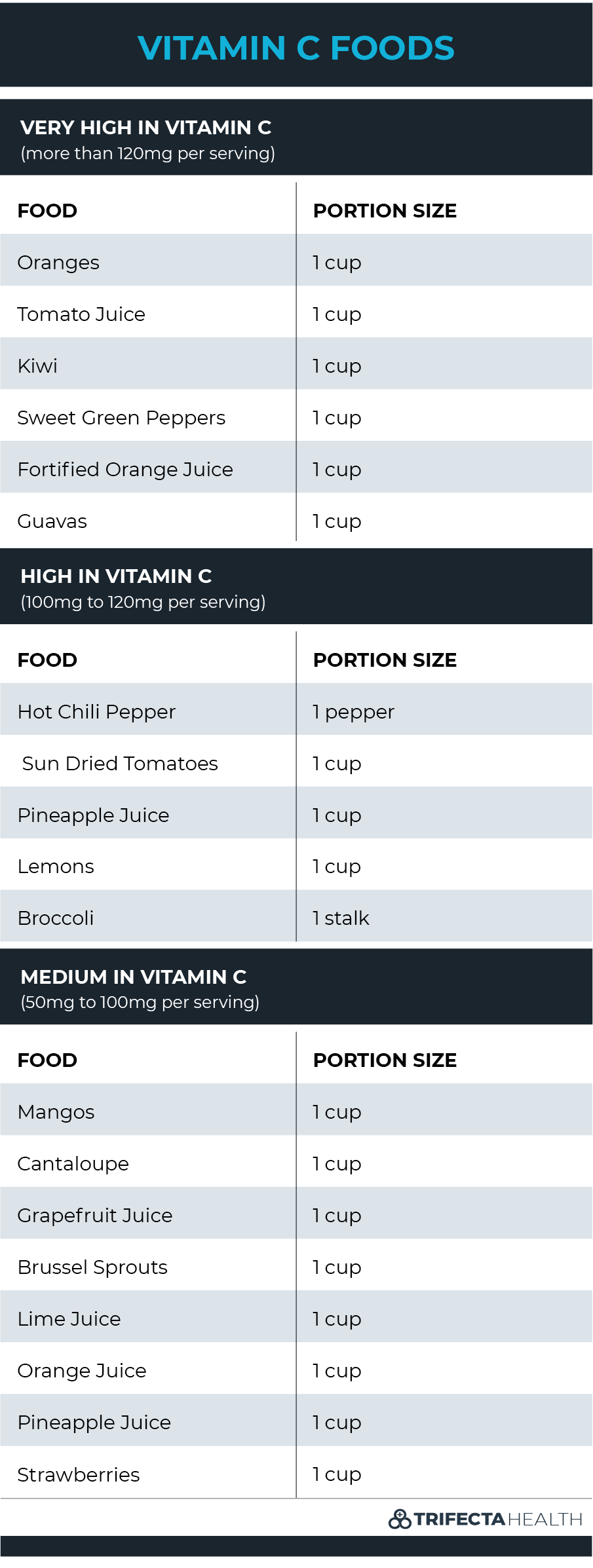
Vitamin C Deficiency
As you may imagine, people who don’t get enough vitamin C can have many problems related to infections, healing, and overall health.
Vitamin C Deficiency Symptoms:
- Poor Wound Healing
- Prolonged Illnesses
- Iron Deficiency Anemia (low red blood cell counts)
- Skin Problems
- Joint Pain
- Dental Problems
- Vision Problems
The most dramatic form of vitamin C deficiency is a condition called scurvy.
Scurvy
Vitamin deficiencies significant enough to cause scurvy are now very rare in the United States and other developed countries. Unfortunately, many people in developing countries around the world who don’t have access to enough nutrient rich food still suffer from this disease.
Symptoms of Scurvy:
- Anemia (low red blood cell counts)
- Bleeding Gums
- Fatigue
- Easy Bruising
- Dental Problems (gingivitis)
- Poor Wound Healing
- Joint & Bone Pain
The most extreme cases of scurvy can lead to neurological problems like seizures and even death (6).
How Much Vitamin C Do You Need?
Recommended daily vitamin C intakes differ by age and risk factors. For example, people who smoke are recommended to take at least 35mg/day more vitamin C than nonsmokers, as this is thought to help the increased damage from toxins in smoke.
| Vitamin C Minimum Recommended Daily Intake | |
| Women | 75mg |
| Men | 90mg |
| Pregnant Women | 85mg |
| Breastfeeding Women | 120mg |
Individuals who smoke require 35 mg/day more vitamin C than nonsmokers.
Some studies support that additional benefits for adults may be seen with higher intake - greater than 500mg daily (8).
Vitamin C Supplements
The technical term for the vitamin is L-ascorbic acid, and this is what you will often see on listed under the ingredients of many supplements of vitamin C powder. Other names you may see associated with vitamin C supplements include mineral ascorbates such as calcium ascorbate and sodium ascorbate. Multivitamins almost always contain enough vitamin C.
Any of these supplements will be effective in providing adequate levels of vitamin C. Research hasn’t shown that any one type of supplement is better than the other (9).
Vitamin C Serum
Because it is so important for our skin health, topical applications of vitamin C are becoming increasingly popular.
There is some evidence to support that some of these serums can be effective at helping the skin in people who are low in vitamin C.
Best Vitamin C Serum
Because it’s so difficult for vitamin C to make it through the skin, many different approaches have been tried. The formulations that seem the most helpful include ascorbic acid at a pH <4. It also seems like liposomal vitamin C (encapsulation into a lipospheric form) is also more effective at absorption.
However, it’s important to remember that people who are getting enough vitamin C in their diet probably won’t significantly benefit from these topical serums (10).
Too Much Vitamin C
Like most things, more isn’t always better.
Our body is overall really good at managing our optimal vitamin C blood levels. When we could use more, our bodies absorb it very effectively - up to 80-90% of the vitamin C we consume. It’s expected that once our daily intake goes above 1gram/day, we start losing about half of it in our urine.
And even if we’re taking in large quantities, our blood levels of vitamin C usually only reach a maximum of about 220 micromol/liter before excreting excess in the urine.
Because our body is so good at eliminating excess amounts, there aren’t many bad consequences of getting too much of this vitamin. Sometimes people may feel an upset stomach, nausea, or diarrhea from very high doses. High levels can also increase the risk of kidney stones from forming.
The unusual exception for this is in people who have a very rare health condition called hemochromatosis. This condition involves an iron overload. Because vitamin C can improve iron absorption, it can also contribute to making hemochromatosis worse (1).
In the end, most of us can get all of the vitamin C we need from eating nutrient rich fruits and vegetables. For those not a fan of brussel sprouts or their daily dose of orange juice, supplementing with a multivitamin or other supplement source is enough to ensure you’re getting all of the nutrients you need.